
Ecommerce Planning: How to Create a Winning Blueprint for Your Online Store
It's important to safeguard your success when starting an online business. Here's a practical guide to help you draft a winning business plan.
By Francesca Nicasio — 11 June, 2021
The ecommerce sector is thriving, and the industry has ballooned into a market with $4 trillion in online sales every year as more customers choose to buy products and services from the comfort of their homes.
Succeeding in the booming ecommerce industry requires comprehensive knowledge of your market niche, excellent strategy, and a solid ecommerce business plan.
Careful research and planning will cement your understanding of your business and help you set measurable targets for your online store. 💵 🛍️
In this article, we will provide you with a practical guide to help you draft a winning business plan that will ensure the success of your online business.
Why is it important to have an ecommerce strategy?
Having a clearly defined strategy for your online store helps you outline where you want to take your business, and the steps you must take to get there.
The chances your business will succeed will also improve immensely when you take the time to develop a blueprint for your venture.
50% of new businesses in the United States fail within the first five years largely because their founders did not start with a solid strategy.
Developing an effective strategy forces you to think critically about every aspect of your new business. This allows you to clarify your ideas, spot potential problems, and leverage opportunities before launching your new business.
Building a strategy will help you identify the right products and services to offer to customers, and the ideal demographic of buyers that will be interested in what you are selling.
You will come to understand critical subjects like product sourcing, supply chain management, customer care, budgeting, and so forth.
With proper research and planning, you can map out your business plan template and set metrics that you will use to track your progress.
What are the types of ecommerce business models?

A business model is a framework that outlines how your business will deliver value to customers in your specific target market.
It describes how you will make money and states the specific customers that will be buying your products and services.
There are five types of business models ecommerce companies can choose from. These models are not silos, and you can adopt a combination of business models that best suit your vision for your store. The five models are:
1. Business to Consumer Ecommerce (B2C)
This is the most popular business model, and here your store sells products to individual consumers. It is similar to what goes on at a brick and mortar store, except the business is conducted online.
There are many businesses in the B2C space, and success depends on quality products, branding, customer care, and effective marketing.
2. Business to Business Ecommerce (B2B)
This model involves selling your products or services to other businesses. You can sell physical goods like stationery, office furniture, or digital products like online courses.
You can also offer services like online coaching, talent recruitment, software development, and others. The primary advantage of the B2B model is that many business customers prefer long-term relationships and are often recurring customers.
This makes long-term planning and budgeting much easier.
3. Customer to Customer Ecommerce (C2C)
Here individual customers use online marketplaces to trade and exchange items.
The company providing the marketplace platform will often take a small commission for facilitating the transaction.
Popular online marketplaces for consumer-to-consumer transactions include Etsy, eBay, Facebook Marketplace, and Craigslist.
This model is a good option if you are just starting out and you don't have the budget to build your own ecommerce store.
4. Consumer to Business Ecommerce (C2B)
This is a model with a growing rate of adoption, and here the consumer sells products or services to businesses.
This model is popular among sole proprietors that sell media products and software tools to businesses.
Examples include digital products like stock photos offered on sites like Flickr or software tools like WordPress plugins sold on the WordPress store.
5. Ecommerce Subscription Model
Here a business regularly delivers product packages or ongoing services to a customer in exchange for recurring payments at clearly specified intervals.
The business will define a package of products or services offered at a price, and the customer will pay a fee regularly to get access to the package.
Most of the businesses that use the subscription model, including Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, Shopify, and others, offer online services or sell digital products.
However, an increasing number of companies that sell physical products online are offering their products as subscription packages.
A good example is Birchbox. Birchbox sells perfumes, beauty products, and skincare products to its customers. The company packages its products as personalized monthly grooming and beauty subscription boxes, and it has been going strong for 10 years.
This model works for both businesses and consumers. The customer gets their choice of products delivered to their doorstep when they need it, and the company gains the reassurance of a predictable revenue stream.
Choosing your ecommerce business model
The best business model for your store will depend on what you are selling, the market you want to compete in, and your finances.
An ecommerce store can sell:
- Physical products: apparel, shoes, jewelry, home accessories, furniture, and food items.
- Digital products: software tools, ebooks, online courses, and media products.
- Services: consulting, outsourcing, content creation, software development, and others.
Look at the type of products or services you are selling, determine the type of customer that will derive value from your offering, and use the insight gained to select the best business model for your store.
What is involved in the ecommerce business planning process?
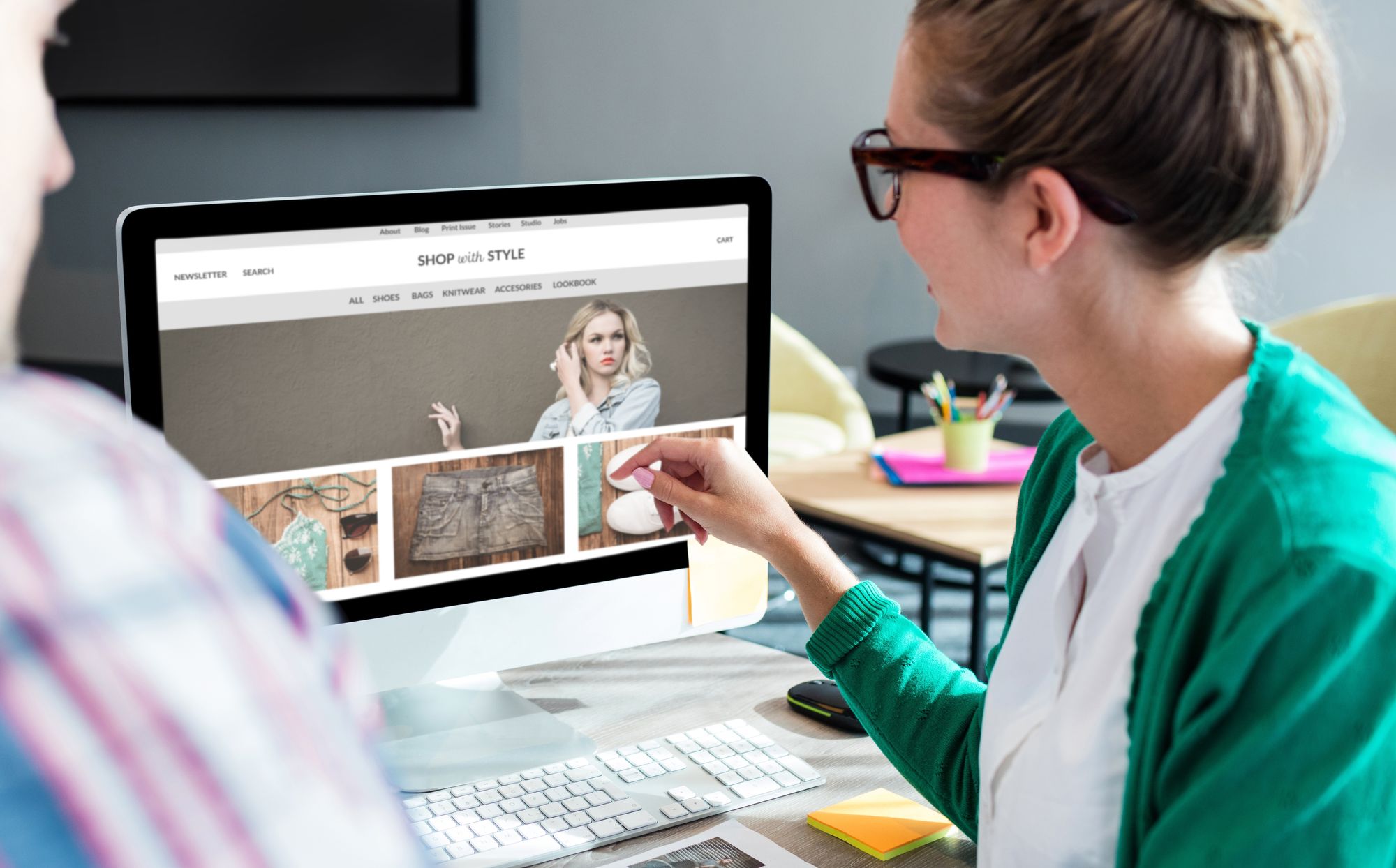
Crafting a comprehensive blueprint for your store requires a firm grasp of the many elements that make up a successful ecommerce business plan.
Below are the steps you must take when developing a strategy for your new business:
Market research
Market research involves getting an overview of your market niche and identifying your competitors.
This is where you look at the trends in your vertical market, discover the factors that affect growth in the sector, and identify the specific sub-niche you are going to serve.
For example, market research will show you that sustainable fashion is one of the fastest-growing sub-sectors in the clothing industry, with a projected 9.1% annual growth rate from 2021 to 2030.
If you plan to start a store selling apparel, such data will show you that the growing awareness of customers about the importance of ethical fashion means branding your store as an eco-friendly company is key to attracting today’s customers.
When developing your market overview, ask the following questions:
- How big is your market niche?
- How well has it grown in the past five years?
- What are the prevailing trends in the sector?
- Which sub-sector has enjoyed the most historic growth?
- Which sub-sectors are poised for future growth?
Analyzing your competition is just as important as understanding the state of your market sector.
Unless you are pioneering a new product, it is highly unlikely that you are the only online player in your market niche. Researching your competitors helps you figure out whether the market is saturated or if there is still room for a new player.
You will also discover the popular products your competitors are offering, the marketing tactics they are implementing successfully, and the hidden opportunities they are missing.
Your competitor analysis should answer the following questions:
- Who are the major competitors in your subsector?
- How crowded is the market niche?
- What products are on offer?
- What new products are missing from the inventory of your major competitors?
- What is the overall quality of the websites of your competitors?
- How good is the customer care service of the major players in the sector?
- What are the popular pricing strategies?
- What strategies are the major players using to market their products?
- What are the popular supply chain management practices in the sector?
- What are the emerging product innovation, sales, and marketing ideas that are yet to gain traction with the major players?
Getting the data you need
Use the sources listed below to get the data you need to develop your industry overview and competitor analysis report:
- Industry reports: search Google for the latest industry reports in your niche. The SBA (Small Business Administration) and companies like Edelman Intelligence publish industry reports annually.
- Online surveys: use online survey tools like SurveyMonkey to collect data directly from your customers. Prepare well-designed questionnaires and use them to ask customers about the trends and products they are interested in.
- Amazon search: Amazon is the world’s largest online retailer, and its search bar is a gold mine for discovering the products customers are buying. Type relevant keywords in your niche into the search bar, and check out the suggestions in the auto-complete box.
- Google Trends: this tool can help you discover the trending products and services in your niche. Type in your seed keyword, and filter according to region, demographics, and duration.
- Social mentions: social media monitoring tools like Awario, Mention, and Brandwatch help you identify the products customers are talking about. You will also discover the demographics of the customers that are interested in those products.
Audience research
Who will visit your store to buy your products, and why? You must identify your customers and find out what they expect from your business.
You need to know what makes your customers tick, and the qualities they expect from brands they follow.
Customer demographic data, including age, education, social media preferences, income level, and geography, is also very important.
The data must tell you:
- Where your customers come from,
- The values of they care about,
- The products and features they expect on your online store,
- The customer care services they need,
- And, how much they are willing to spend on the products you sell every month.
The best way to get the information you need is to ask customers directly. Use online surveys, focus groups, and in-person interviews to build a profile of each customer segment.
Creating buyer personas for each customer segment will help you develop custom marketing strategies for each customer grouping.
Your research must provide useful insights that will influence your marketing campaign and ensure high conversion rates.
Product development and sourcing
Researching your target audience and proper market research will help you identify the best combination of products for your product line. The next step is to figure out how you will source the products you plan to offer on your store.
Ecommerce product sourcing options include:
In-house manufacturing
Here you make your own products and control the quality of the goods that are coming out of your factory.
In-house manufacturing lets you offer customized products to customers, maintain quality requirements, and adapt quickly to changing product innovation trends.
The major downsides are the huge capital outlay required to set up your factory, and the additional overhead costs for keeping factory personnel on the payroll.
Third-party manufacturer
You outsource product manufacturing to a contracted manufacturer that will produce and ship your products to your warehouse, the customer, or a third-party marketplace like Amazon.
This sourcing option helps you reduce costs, easily ramp up production in response to increasing demand, and leverage the manufacturing expertise of third-party manufacturers.
The major disadvantages are the limited control over the quality of your products, and the security risk when using customer data.
Dropshipping
Here you purchase the product listed on your store from a supplier who ships the product to your customer.
You list the product on your store, a customer orders the product, and you buy it from a supplier that will fulfill your customer’s order.
It is a very convenient method where you never actually stock the products you are selling yourself. This sourcing method is very popular because zero inventory management costs make it easy to get started.
You can offer a wide range of products and only make purchases to fulfill customer orders when needed.
The disadvantages include customer service issues, shipping complexities, and low-profit margins because of intense competition.
Wholesale
Under this sourcing model, you buy products in bulk from a supplier at a discount, store them in your warehouse, and ship them to customers when orders come in.
This sourcing option requires significant capital outlay to purchase and store your inventory. It works when the product you are selling is in high demand and you have an established customer base.
White labelling
Here you have a license to package and sell a generic product in your own name.
You don’t manufacture or own the product, but you can design the product packaging and put your name on the product.
This works when you are sure there is demand for the product, and you can carve out a loyal base of customers that will buy from you.
Branding, effective promotional tactics, and excellent customer service can let you command higher margins using this method.
Logistical planning
The type of product you sell on your ecommerce store will shape your logistical planning.
If you offer services, you need to provide tools on your website that let customers schedule appointments and book your services.
If it's digital products you sell, you need to figure out how you will develop your products and how customers will access them.
Ecommerce businesses that sell physical products must plan for:
- Production: select the best product sourcing method for your business.
- Suppliers: how will you get the raw materials for your products? Will you work with local or international suppliers?
- Inventory management: will you store your products yourself? What inventory levels should you maintain? What software tools will you use to track incoming and outgoing inventory?
- Shipping and Fulfilment: how long will it take to get your products to customers? What shipping times should you offer to customers? Will you ship to international customers?
- Customer Support: what are the types of customer support services you will offer? How will you track and respond to customer requests, returns, and refunds?
Pricing strategy
Your pricing strategy can determine the success or failure of your business.
Your product price must be competitive enough to woo customers while incorporating an adequate premium to ensure you make a profit.
To set the right price for your product, you must factor in all the operational costs incurred in producing, marketing, and shipping your product to the customer.
There are five popular ecommerce pricing strategies you can choose from, and they are:
Cost-based pricing
You will add a fixed markup on top of the production cost of each unit and price your product accordingly. This strategy is simple to implement and ensures you will make a profit.
However, it is too business-focused, and it does not take changing customer demand or competition into consideration.
Competition-based pricing
This entails pricing your product to closely match the prices offered by your competitors.
Competitor analysis will help gain a good understanding of how your competitors are pricing their products.
You can choose to price lower to attract frugal customers or offer a better quality product at a higher price. You can also choose to match the prices of your competitors if the market is big enough for you to attract buyers.
Value-based pricing
This involves pricing your product according to the value you are offering to customers. The strategy relies on brand awareness and customer loyalty.
Adopting value-based pricing means you must offer products of superior quality and offer extra features that differentiate your products from other alternatives.
Dynamic Pricing
This is a proactive strategy where you constantly adjust product prices in response to market demand and competitor prices.
This strategy lets you set the product price best suited for the prevailing market conditions in real-time. The downside is that prices can get so low that you may have to sell your product at a loss.
Repricing tools like RepricerExpress and Aura let you automate the process by setting rules for the software to follow in different market conditions.
Bundle Pricing
Following this strategy, you will bundle complementary products together and offer the package at a discounted price.
The price of the bundled package will be lower than the individual prices of the products if they were purchased separately.
This strategy offers value to buyers and boosts sales, but you must factor in the possibility that you will find it harder to sell the products at their original prices in the future.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan must examine how you plan to fund your business, and include a forecast section showing projected sales, operational costs, and net income.
Pinpointing where you will source your startup costs is essential. You can bootstrap your business with your own funds, or seek outside funding from any of the following sources:
- Angel investors
- Wealthy business partners
- Business loan
- Crowdfunding
- Venture capital
Your projected expenses should cover:
- Warehouse rent expenses
- Employee pay
- Cost of office supplies and other work-related expenses
- Cost of production and shipping
- Advertising budget
- Cost of marketing software tools
- Cost of ecommerce platform subscription
Use estimated revenues and expense projections to prepare a projected profit-and-loss statement. Your financial plan and the projected profit-and-loss statement will be very important if you are seeking outside funding.
Choosing an ecommerce platform
Ecommerce platforms are sales channels that give you the tools to create your online store and sell your products to customers.
There are three major ecommerce sales channels including:
WooCommerce
WooCommerce is a very popular open-source ecommerce platform that is built on WordPress. The free plugin powers 28% of all online stores on the internet, and its popularity is due to the vast customization options available to users.
You can pick from thousands of free and paid extensions to add the features you want to your store. The platform is developer-friendly, and you can customize the plugin to build the exact store you want.
Shopify
Shopify is a plug-and-play ecommerce platform that provides you with all the tools you need to set up your ecommerce site, find customers, and make sales.
It is subscription-based, but there plans for everyone with the Shopify Lite plan starting at $9 per month. To access the full power of the platform, you need to pay $299 per month.
Shopify is great because you can set up your store in minutes with no coding knowledge, and there is a wealth of resources online to help you navigate any issues.
The downside is that it doesn't offer the breadth of customization options and access to third-party extensions you will get when using WooCommerce.
Magento
It is an open-source ecommerce platform that provides users with powerful tools to create unique and feature-packed online stores.
Building an online store with Magento requires coding expertise, but its enterprise-grade features have made it very popular with large ecommerce brands.
Go for Magento, if you need the flexibility to customize your CMS extensively to meet the unique needs of your business.
Marketing plan
Your marketing plan will outline how you will get your brand in front of your target customer and convince them to visit your store to buy your products.
Branding is the heart of any marketing plan. It encompasses the symbols and design themes that differentiate your store from your competitors.
Your pricing strategy, product quality, and USP are all important elements of your brand.
When designing your store, focus on design elements like your logo, color palette, typography, site visuals, and brand language to distinguish your store.
Your marketing strategy should cover:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
You won’t make sales if customers can't find you online. The key to successful SEO is keyword research, and how keywords are integrated into product pages, descriptions, metadata, and blog posts.
You can handle SEO yourself or outsource your SEO campaign to an SEO consultant.
Content marketing strategy
Your content strategy will shape how you will create and use content in your online marketing campaign.
Define the brand voice that will shape your website copy, social media content, and the articles published on your blog. A style guide that sets rules for writing and formatting content will ensure consistency.
You must also decide whether you will handle content creation in-house or outsource it to a content creation agency.
Social media
Use your customer research data to identify the social media platforms that are popular with your target customers. Use social media monitoring tools to discover the products and social issues that your customers like to discuss.
Create a winning social media strategy that will outline the type of content you will post, how often you will post, and how you will engage with your followers.
Paid advertising
This includes affiliate marketing, influencer marketing, Pay per click (PPC) advertising, and social media ads.
Paid marketing strategies tend to get results quickly, and you can use any combination of marketing channels to promote your store and build awareness about your new business.
Customer research will help you target the right customers with your promotional ads.
Email marketing
Email marketing has a far higher ROI than other marketing strategies and it returns $44 for every dollar invested.
An effective email marketing strategy is crucial to the success of your online store. Your email strategy will outline how you will:
- Encourage email sign-ups,
- Inform customers about new products,
- Promote your customer loyalty program,
- Follow up customers with abandoned carts,
- and provide after-purchase information to buyers.
There are email marketing software tools like Mailchimp and Aweber that will help you set up and manage your email marketing campaign.
An effective digital marketing strategy that leverages the marketing channels listed above will drive traffic to your ecommerce store and achieve high conversion rates.
Conclusion
Building a successful ecommerce store is not always easy, but if you take it one step at a time and apply the knowledge you have gained from this article as a template to craft your business blueprint, you will have your store up and running in no time.